- These allow the inclusion of the entire population as eligible for randomization. Consequently, the whole study population who meet the eligibility criteria, is randomly assigned to the different treatment groups (experimental and control treatment group) regardless of biomarker status.
- They allow assessment of treatment benefit for the entire population irrespective of biomarker status whilst at the same time allowing for treatment benefit to be tested in the two biomarker-defined subgroups separately.
- Generally, they are useful when at least one of the following criteria exists: when we are uncertain about the benefit of the experimental treatment in the overall population versus the biomarker-defined subgroups, the targeted treatment may benefit both biomarker-positive and biomarker-negative patients, the goal is to test the predictive ability of a biomarker, the assay reproducibility and accuracy is questionable, the turnaround time for biomarker assessment is long and the biomarker prevalence is high.
Alternative names: all-comers/untargeted/unselected/non-targeted/simple randomization designs
Categories
Variations:
Two-way stratified designs
View more details by clicking on image to fully expand. Then hover over boxes for info.
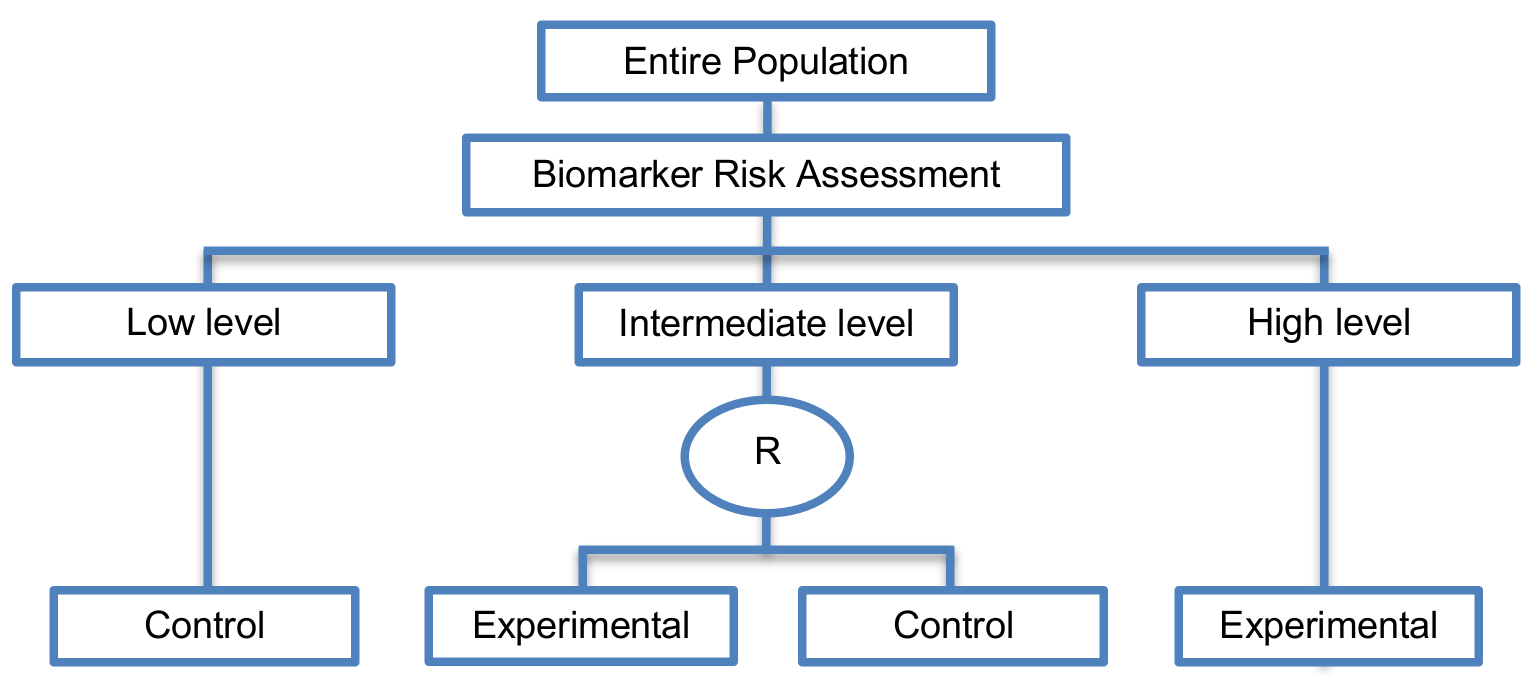
- An example of an actual trial which uses this approach (i.e. Patients are stratified according to their biomarker results. Standard treatment is tailored to patients with a low score, experimental treatment is given to patients with a high score and those with an intermediate score are randomized to either experimental or standard treatment) is that conducted by the “Arbeitsgemeinschaft Gynakologische Onkologie” (AGO) Study Group in cooperation with the EORTC Receptor and Biomarker Study Group for the “Chemo-N0 trial” to validate UPA and PAI1 as prognostic indicators in node negative breast cancer.
- According to Spira et al. a noninferiority design for the intermediate group can be used and has the statistical power to detect a 3% or greater difference between the randomized arms. Since there is no direct prospective comparison between the novel and standard classifier, the two-way stratified designs provide further, although indirect, validation of the biomarker.

